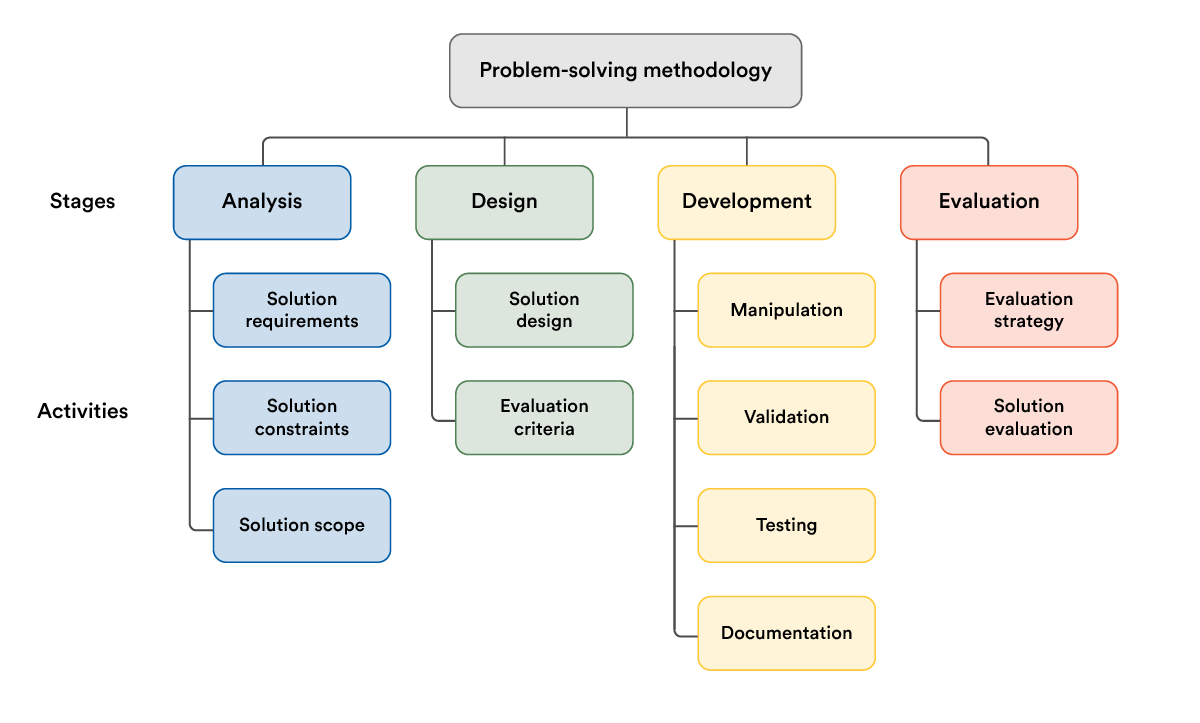
 The problem-solving methodology is a core concept used throughout VCE.
The problem-solving methodology is a core concept used throughout VCE.
When designing software, you need to take this stage by stage, achieving the activities required in each stage.
Important
Unit 3 only covers the stages Analysis and Design. Unit 4 covers the rest.
Analysis
What is required of the software? What does your software need? What can’t the software do?
During the analysis stage of the PSM, you need to answer these questions and find out what your software should be designed to do.
Solution requirements
What must be done by the solution? What does the client need the software to do?
You must determine the solution requirements, which is split into
- Functional - the solution does what the client needs.
- Non-functional - refers to requirements in relation to UX, UI and stability of the solution such as:
- User experience (UX)
- reliability
- portability
- robustness
- maintainability
Solution constraints
What can’t be done by the software? Why can’t something be included in a solution?
A solution’s constraints could be:
- cost
- speed
- requirements of users
- legal requirements
- security
- compatibility
- user’s expertise with the solution
- equipment’s availability and capacity
Solution scope
The scope determines the boundaries or parameters of the solution.
- What must the solution provide?
- What can’t the solution provide?
- Benefits of the solution