Introduction
To find the shortest path between a picked node and all other nodes in a weighted graph. Starting from a specified node, it calculates the distances between itself and all other nodes in a graph.
How it works:
- Starting at 1 (A), calculate distances. This is known as the source.
distances = {"1": 0, "2": 7, "3": 9, "4": inf, "5": inf, "6": 14}
unvisited_nodes = {"2", "3", "4", "5", "6"}
visited_nodes = ["1"]-
Travel to the next unvisited node with the shortest distance from the source. In the first iteration, it will be node
2, as it has the distance of7. -
Calculate the distance for each unvisited node of the current node (cost of path to current node + to unvisited neighbour). If the calculated distance is less than the pre-existing value, update distances.
# First iteration
distances = {"1":0, "2": 7, "3": 9, "4": 22, "5": inf, "6": 14}
visited_nodes = ["1", "2"]
# 3 and 4 is reachable from the current node of 2. However, it costs more to travel to 3 from 2 (7+10 > 9), so the pre-existing distance of 9 will be kept. 4 is now reachable with the cost of 7 + 15 = 22 which is < inf, so it will be updated.- Go back to step 2, starting the next iteration.
# Second iteration
current_node = "3" # 3 is the next node with shortest distance of 9
distances = {"1":0, "2": 7, "3": 9, "4": 20, "5": inf, "6": 9+2}
visited_nodes = ["1", "2", "3"]
# Third iteration
current_node = "6" # 6 is the next node with shortest distance of 11
distances = {"1":0, "2": 7, "3": 9, "4": 20, "5": 11+9, "6": 11}
visited_nodes = ["1", "2", "3", "6"]
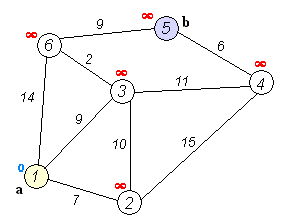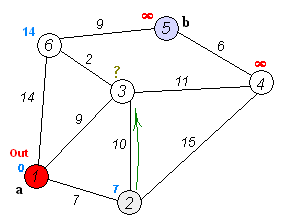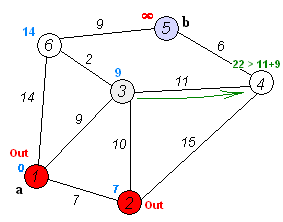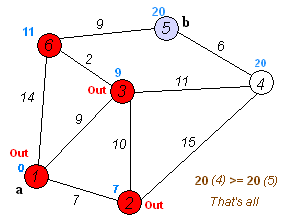
# Fourth iteration
current_node = "4" # 4 is the next node with the shortest distance of 20
distances = {"1":0, "2": 7, "3": 9, "4": 20, "5": 20, "6": 11} # no updates
visited_nodes = ["1", "2", "3", "6", "4"]
# Fifth iteration - because there are no more unvisited nodes, there isn't a 5th iteration.
return distances # therefore, the distances from A to all other nodes are defined in distances.Sample code
I personally wrote this, so it’s definitely not the best way of doing Dijkstra’s, but it’s definitely a method.
# Define a matrix to represent distances between nodes
matrix = {
"A": {"A": 0, "B": 7, "C": 9, "D": None, "E": None, "F": 14},
"B": {"A": 7, "B": 0, "C": 10, "D": 15, "E": None, "F": None},
"C": {"A": 9, "B": 10, "C": 0, "D": 11, "E": None, "F": 2},
"D": {"A": None, "B": 15, "C": 11, "D": 0, "E": 6, "F": None},
"E": {"A": None, "B": None, "C": None, "D": 6, "E": 0, "F": 9},
"F": {"A": 14, "B": None, "C": 2, "D": None, "E": 9, "F": 0}
}
def dijkstra(matrix, source):
# Get the distances from the source node to all other nodes
start_vertex = matrix[source]
print(start_vertex)
# Initialize distances from the source to all nodes
# If there is no direct path, set the distance to infinity
distances = {node: start_vertex[node] if start_vertex[node] is not None else float('inf') for node in matrix}
# List to keep track of visited nodes
visited_nodes = [source]
# Variable to keep track of the number of iterations
iteration = 0
# Loop until all nodes have been visited
while len(visited_nodes) < len(matrix):
print("\n")
iteration += 1
print("Iteration: ", iteration)
print("Visited nodes: ", visited_nodes)
print("Distances: ", distances)
# Initialize the minimum distance to infinity
min_distance = float("inf")
min_vertex = None
# Get the list of potential nodes to visit next
potential_nodes = [node for node in distances if distances[node] != None and node not in visited_nodes]
print("potential nodes:", potential_nodes)
# Find the node with the smallest distance
for node in range(len(potential_nodes)):
if distances[potential_nodes[node]] < min_distance:
min_distance = distances[potential_nodes[node]]
min_vertex = potential_nodes[node]
print("min_vertex: ", min_vertex)
visited_nodes.append(min_vertex) # add minimum vertex to visited nodes
neighbours = [node for node in matrix[min_vertex] if matrix[min_vertex][node] != None and node not in visited_nodes] # check neighbours of miminum vertex
print("neighbours: ", neighbours)
for node in neighbours:
print("node:", node, matrix[min_vertex][node])
# if current distance is larger than new path, then update it.
if distances[node] > distances[min_vertex] + matrix[min_vertex][node]:
distances[node] = distances[min_vertex] + matrix[min_vertex][node]
return distances
print(dijkstra(matrix, "A"))Transclude of dijkstra.py